 Build a boundary based statistical model to predict a categorical outcome (classify) as a function of multiple predictor variables. SVM is able to create much more flexible boundary shapes than the Classification Tree (Partition) and Discriminant Analysis method.
Build a boundary based statistical model to predict a categorical outcome (classify) as a function of multiple predictor variables. SVM is able to create much more flexible boundary shapes than the Classification Tree (Partition) and Discriminant Analysis method.
Support Vector Machines
- From an open JMP® table, select Analyze > Predictive Modeling > Support Vector Machines.
- Add a nominal or ordinal response variable from Select Columns to the Y, Response role.
- Add candidate predictor variables to the X, Factor role.
- If desired, enter a validation column into the Validation role as shown in this example. Click OK.
- The Model Launch control panel opens allowing a choice of a Kernal Function and associated options. Default settings were used for this example. Click Go. JMP displays:
- Response Profile Plot displaying the classification regions and the data values for two of the predictor variables. These can be changed to other variables by selecting the red triangle next to the variable name on the axes. Levels for all the remaining predictors can be changed with the sliders above the plot.
- Model Summary (not shown) and a Confusion Matrix detailing the classification performance.
Additional options, such as ROC and Lift Curves, Profilers, Save Predicteds, Save Prediction Formula, Save Probabilities, as well as Publish Probability Formulas are accessible from the red triangle.
 Equity.jmp (Help > Sample Data Library)
Equity.jmp (Help > Sample Data Library)

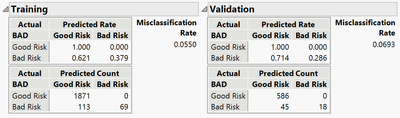
Intepretation:
• There are 649 observations in the Vaidation Data. Of these, 45 (6.9%) where misclassified. 45/(45+18) = 71% of the Bad Risk customers were misclassified as Good Risk. 0/(0+586) = 0% of the Good Risk customers were misclassified as Bad Risk.
Note: The default rule is to classify an observation in the class with the highest estimated probability of being in that class (i.e., Prob > 0.50). It is advantageous to evaluate different cutoff values in order to minimize a specific type of misclassificaiton rate over another. In this example it would be much better to choose a cutoff level to create a lower misclassification rate for Bad Risk Customers misclassified as Good Risk while accepting a higher misclassification rate for the other. This analysis can be performed by saving the predicted probabilities to the data table and using the calculator tool to create a conditional argument to conclude an outcome based on those predicted probability values.
Visit Predictive and Specialized Models > Support Vector Machines in JMP Help to learn more.