This guide demonstrates how to find the area under the normal curve using formulas and the Distribution Calculator.
Column Formula for Area Under a Normal Curve (One Value)
1. Select File > New > Data Table.
2. Add one row - select Rows > Add Rows, and type “1”. Click OK.
3. Right-click on Column 1, and select Formula to access the Formula Editor.
4. From the function list on the left, select Probability > Normal Distribution.
This will give the following formula, which returns the probability that a normally distributed random variable is less than q.:


5. Click the caret  on the keypad twice to add fields for the mean and standard deviation.
on the keypad twice to add fields for the mean and standard deviation.

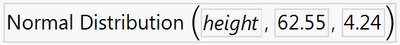
6. In the fields provided, enter the value of q, the mean, and the standard deviation. Click OK.
• JMP® will populate the row in the data table with the cumulative probability value (the area under the lower tail of the normal curve).
Note: To find the area in the upper tail, or the area between two values, use the following formulas:
• Upper tail:

• Between two values:

Note: The Distribution Calculator provides an interactive tool to calculate and visualize areas under various distributions (shown on the right). See the “Interactive Tools for Teaching and Learning” guide in “Chapter 2: JMP Basic” to learn how to access.

Column Formula for Area under a Normal Curve (for a Column of Values)
1. Open an existing data table (File > Open), or open a new data table (File > New > Data Table) and create a column of values.
2. Select Cols > New Column to create an additional column, and rename the column. We’ll name our column Prob Height.
3. Click Column Properties, and select Formula to access the Formula Editor.
4. Complete the formula using one of the two options shown to the right (type in the mean and standard deviation values into the appropriate fields or use the Col Mean and Col Std Dev functions. JMP will populate the new column with cumulative probability values for each value in the column.
 Big Class.jmp (Help > Sample Data Folder)
Big Class.jmp (Help > Sample Data Folder)

Visit Using JMP > Create Formulas in JMP in JMP Help to learn more.