- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Printer Friendly Page
Discussions
Solve problems, and share tips and tricks with other JMP users.- JMP User Community
- :
- Discussions
- :
- Re: R-Square (U) In Contingency Tables
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Get Direct Link
- Report Inappropriate Content
R-Square (U) In Contingency Tables
Hey All,
I had a question about the R-square uncertainty ratio in Contingecy Tables (placed in same table as DOF and loglikelihood). I am currently doing research where I've found significance in my p-value (alpha=.05), but the R-square value is close to 0. Now, I am aware that in continuous vs continuous, an R-value is used to determine the correlation between the two variables.
My question is: What relevance does the Rsquare value in a contingecy table have on my conclusions?
I was able to reject the null hypothesis via my p-value, but as I previously mentioned, the Rsquare is very close to 0, which makes me unsure if I should proceed with the alternative hypothesis in mind.
Thanks in advance!
Accepted Solutions
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Get Direct Link
- Report Inappropriate Content
Re: R-Square (U) In Contingency Tables
You may interpret the RSquare (U) the same way as you would interpret the RSquare from a linear regression. The RSquare is based on sums of squares: SS(model) / SS(total). RSquare (U) likewise is -L(model) / -L(reduced). It tells you the proportion of the total uncertainty that is accounted for by the model, assuming it is the correct model.
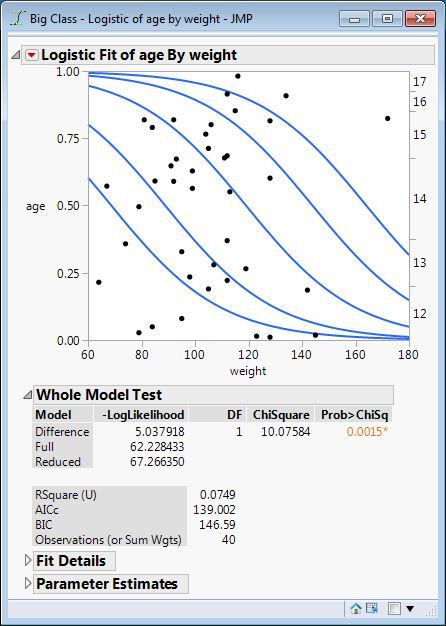
This relationship is easier to see in Logistic Fit than in Contingency because Contingency only reports the -L(model). This is the analysis of age by weight from Big Class sample data table:
The -L(model) above is labeled Difference here. The -L(total) above is labeled Reduced here. The RSquare (U) is therefore Difference / Reduced = 5.037918 / 67.266350 = 0.0749.
It is common for a statistically significant model of a categorical response to exhibit a very low RSquare (U) as this example demonstrates. Like its continuous model RSquare counterpart, it indicates the performance of the conditional prediction over the marginal prediction.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Get Direct Link
- Report Inappropriate Content
Re: R-Square (U) In Contingency Tables
You may interpret the RSquare (U) the same way as you would interpret the RSquare from a linear regression. The RSquare is based on sums of squares: SS(model) / SS(total). RSquare (U) likewise is -L(model) / -L(reduced). It tells you the proportion of the total uncertainty that is accounted for by the model, assuming it is the correct model.
This relationship is easier to see in Logistic Fit than in Contingency because Contingency only reports the -L(model). This is the analysis of age by weight from Big Class sample data table:
The -L(model) above is labeled Difference here. The -L(total) above is labeled Reduced here. The RSquare (U) is therefore Difference / Reduced = 5.037918 / 67.266350 = 0.0749.
It is common for a statistically significant model of a categorical response to exhibit a very low RSquare (U) as this example demonstrates. Like its continuous model RSquare counterpart, it indicates the performance of the conditional prediction over the marginal prediction.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Get Direct Link
- Report Inappropriate Content
Re: R-Square (U) In Contingency Tables
Awesome,
Thank you!
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Get Direct Link
- Report Inappropriate Content
Re: R-Square (U) In Contingency Tables
@Mark_Bailey Can you explain how to interpret the R^2(U) value? R^2 tells how much variability can be explained by the equation if I understand correctly, so is the R^2(U) saying the same for a logistics regression? Given that this value is much smaller, how would you interpret how meaningful this is? I am working with ecological data for context. Do you know if when reporting a model, would you want to use the R^2(U) or the R^2 (which I found in the Fit Stepwise window)- which number is more relevant for a logistics regression?
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Get Direct Link
- Report Inappropriate Content
Re: R-Square (U) In Contingency Tables
Logistic regression is used with categorical responses. It is analogous to linear regression for a continuous response, but not exactly the same. The linear regression analysis of variance is based on the sum of square deviations. The R square sample statistic is the ratio of the model sum of squares to the corrected total sum of squares. It assumes that error sum of squares does not include any fixed effects that were not included in the model. That is to say, it assumes that the model is unbiased. This is important because the sum of squares depend on the selected model. R square is a measure of performance of prediction.
The R square (U) is based on the negative log likelihood or uncertainty (U) of the model parameters. This sample statistic is the ratio of the difference in the log likelihood of the full and reduced models to the log likelihood of the reduced model. Like the linear regression case, it assumes that there is no significant lack of fit by deviance. R square (U) is also a measure of performance of prediction.
I do not see how you can get the R square for a logistic model. The Generalized R Square is an attempt to provide a value that is closer to what one expects from linear regression. Is that the value you refer to? The meaning and interpretation of the adjusted value is not clear.
Broadly speaking, the R square (U) for a categorical response is often very low for a model with significant predictors and no lack of fit. It means that there is large uncertainty in the predicted response.
Recommended Articles
- © 2026 JMP Statistical Discovery LLC. All Rights Reserved.
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Statement
- Contact Us