This guide provides instructions on performing a randomization test (also known as a permutation test) – a resampling method for estimating the sampling distribution of a statistic to generate a confidence interval and a p-value for a hypothesis test. Randomization Testing is available from many JMP reports.
Randomization Testing
Here, we describe how to conduct a randomization test for two means using Fit Y by X.
- From an open JMP data table, right-click on the column header for the Nominal X variable (in this example, sex) and select New Formula Column > Random > Sample With Replacement. This creates a new formula column, Resample[sex].
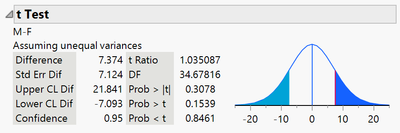
- Conduct a 2-Sample t-Test using the Fit Y by X platform. For this example, the Y, Response is Weight and the X, Factor is sex. See the page: Two Sample t-Tests and CIs for information on how to conduct this test and interpret results.
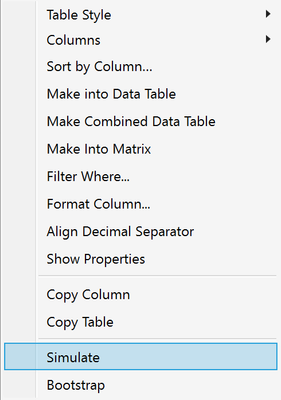
- In the analysis report window, right-click over the statistic of interest and select Simulate. Here we right-click on the column of output containing the Difference (between means).
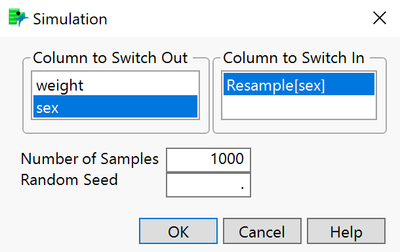
- In the Simulation window, select the column to switch out (sex) and the column to switch in (Resample[sex]), enter the desired number of samples (1000, in this example), and the random seed (if desired), and click OK.
- JMP re-runs the analysis for each sample. For each iteration, the values of the X, Factor (sex) are resampled with replacement.
- The results are stored in a data table with statistics for the original sample and each of the resamples. The SimID• column identifies the resample number.
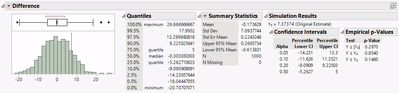
- Use the Distribution platform to explore the results for the statistics of interest. Confidence intervals for the original estimate (the Difference, in this example) are provided, along with empirical (observed) p-values.
Interpretation: The empirical p-value for the two-tailed test is 0.3530. That is, 35.3% of the observed resampled differences were as extreme or more extreme than the difference we actually observed (7.37).
 Big Class.jmp (Help > Sample Data Library)
Big Class.jmp (Help > Sample Data Library)
The Randomization Testing Add-in available in the JMP User Community (community.jmp.com) provides a tool to perform randomization tests for common hypothesis tests in JMP.
Visit Basic Analysis > Simulate in JMP Help to learn more.