- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Printer Friendly Page
Discussions
Solve problems, and share tips and tricks with other JMP users.- JMP User Community
- :
- Discussions
- :
- How to determine sample size for known defect size?
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Get Direct Link
- Report Inappropriate Content
How to determine sample size for known defect size?
We are currently testing some chips and have a high open short failure. We are taking a sample size of 60% of the original lot and performing a sample test. Our unaccepatable defect rate for whole lot is 0.3%. I want to know with a lot size of 8000 or 10000 and a sample size of 60% of this lot size. What will be my defect rate should be to determine my whole lot has a defect rate of 0.3%.
Example
Lot Size : 8000 or 10000
Sample size: 60% of Lot Size
How do determine whats my sample defect rate which will indicate that my lot has 0.3% defect rate.
A JMP or Excel formula instruction will be useful
Accepted Solutions
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Get Direct Link
- Report Inappropriate Content
Re: How to determine sample size for known defect size?
A sample size determination is made in the context of a statistical hypothesis test. This context means that you have to specify the hypothesized proportion and the smallest change in the proportion that is important to you. You also have to specify the desired power in the test. That is, the probability that you will find the difference to be significant when in fact the true difference is at least as large as you specified.
- Select DOE > Design Diagnostics > Sample Size and Power.
- Click One Sample Proportion.
- Enter the significance level desired (default is alpha = 0.05).
- Enter the hypothesized proportion, 0.003 (for 0.3%) in this case.
- I would use the default estimation method.
- Select one-sided if you are interested in an upper bound or two-sided if you want an interval.
- Leave the Null Hypothesis empty.
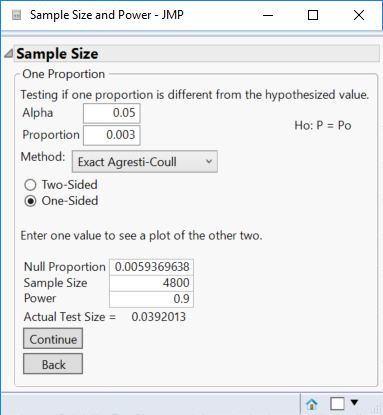
- Enter 4800 for the Sample Size (60% of 6000).
- Enter 0.9 for the Power.
- Click Continue.
Here is the result:
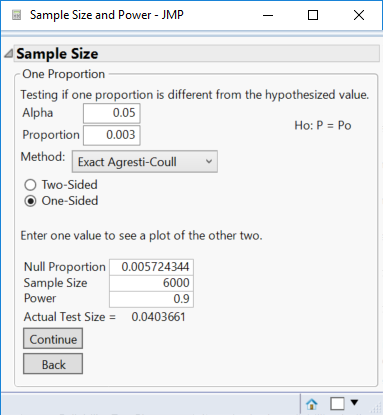
This means that you have 90% of finding a change to 0.59% failures with this sample size. Changing the sample size to 6000, the null proportion decreases to 0.57%:
See JMP Help or this white paper for more details.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Get Direct Link
- Report Inappropriate Content
Re: How to determine sample size for known defect size?
A sample size determination is made in the context of a statistical hypothesis test. This context means that you have to specify the hypothesized proportion and the smallest change in the proportion that is important to you. You also have to specify the desired power in the test. That is, the probability that you will find the difference to be significant when in fact the true difference is at least as large as you specified.
- Select DOE > Design Diagnostics > Sample Size and Power.
- Click One Sample Proportion.
- Enter the significance level desired (default is alpha = 0.05).
- Enter the hypothesized proportion, 0.003 (for 0.3%) in this case.
- I would use the default estimation method.
- Select one-sided if you are interested in an upper bound or two-sided if you want an interval.
- Leave the Null Hypothesis empty.
- Enter 4800 for the Sample Size (60% of 6000).
- Enter 0.9 for the Power.
- Click Continue.
Here is the result:
This means that you have 90% of finding a change to 0.59% failures with this sample size. Changing the sample size to 6000, the null proportion decreases to 0.57%:
See JMP Help or this white paper for more details.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Get Direct Link
- Report Inappropriate Content
Re: How to determine sample size for known defect size?
You supplied a number of specific items about the situation but it is still not completely clear what you are dealing with. For example, if your situation was such that you had a historical failure rate of 0.1% and recently suspected that it had risen to 0.3%, then you would change my instructions so that the Proportion is set to 0.001 and the Null Proportion is set to 0.003 so that you could either determine the minimum sample size given the desired power or determine minimum power given the sample size.
Recommended Articles
- © 2026 JMP Statistical Discovery LLC. All Rights Reserved.
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Statement
- Contact Us