Market researchers use surveys to collect data about products and services. A survey, as a data collection process, consists of two dimensions: questions about the respondents (i.e. who answers the questions) and questions about the products and services (i.e. what you ask). The questions usually asked include: demographics (e.g. age, income, and gender) so that you can assess how closely your respondents resemble your population of interest, and the study questions to gather information to help answer your study objective.
You collect information about how customers use products or services, how satisfied they are with your offerings, and what new features they might desire. The resulting insights let you create better products and services, happier customers, and more revenue for your organization. Putting behavioural analysis at the center of decision making, speeds up time to market and helps maintain a competitive edge. The Consumer Research platform provides a full suite of tools for analyzing consumer and behavioral research data.
- Categorical Platform
- Choice Models
- MaxDiff Platform
- Uplift Platform
- Multiple Factor Analysis

Categorical Platform
The Categorical platform enables you to tabulate, plot and compare categorical responses in your data, including multiple response data. You can use this platform to analyze categorical response data such as defect records, survey responses and to study participant demographics.
This chart shows the results for the simple response survey question “What is your favorite color?” grouped by gender. Each respondent was asked to select one color from the following list: Red, Blue, Green, Orange, Yellow, Pink, Purple or None.
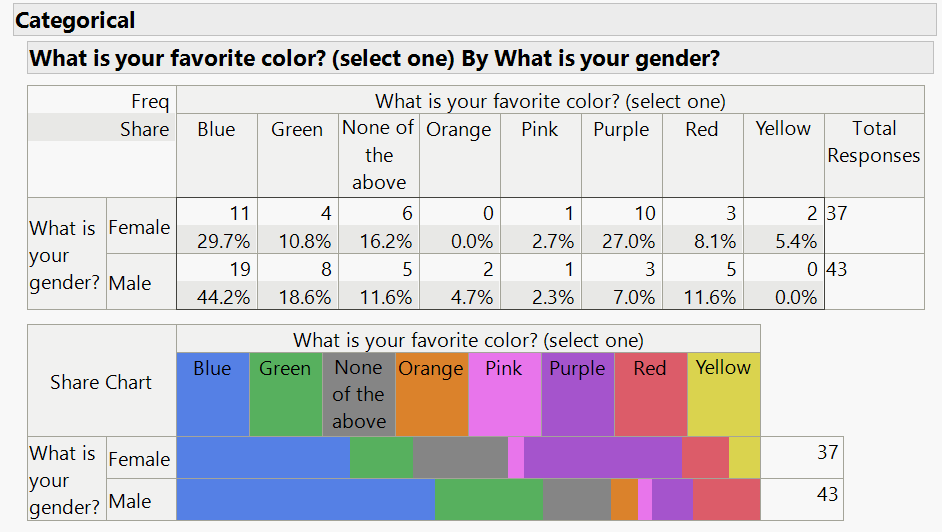
The analysis shows that blue is the favorite color for both genders. For males, the frequency of the 43 male respondents selecting blue is 19. This corresponds to a share of 44.2%. For females, 11 of 37 female respondents (frequency) or 29.7% (share) selected blue. Interestingly, 11 respondents or around 14% selected None for colour.
Choice Models
Choice modelling, is a powerful analytic method used to estimate the probability of individuals making a particular choice from presented alternatives. Choice experiments are used in market research to help discover which product or service attributes your potential customers prefer; using 0 or 1 response indicator.
The Effect Summary report shows the effects in order of significance. Speed is the most significant effect, followed by Price and Disk Size.
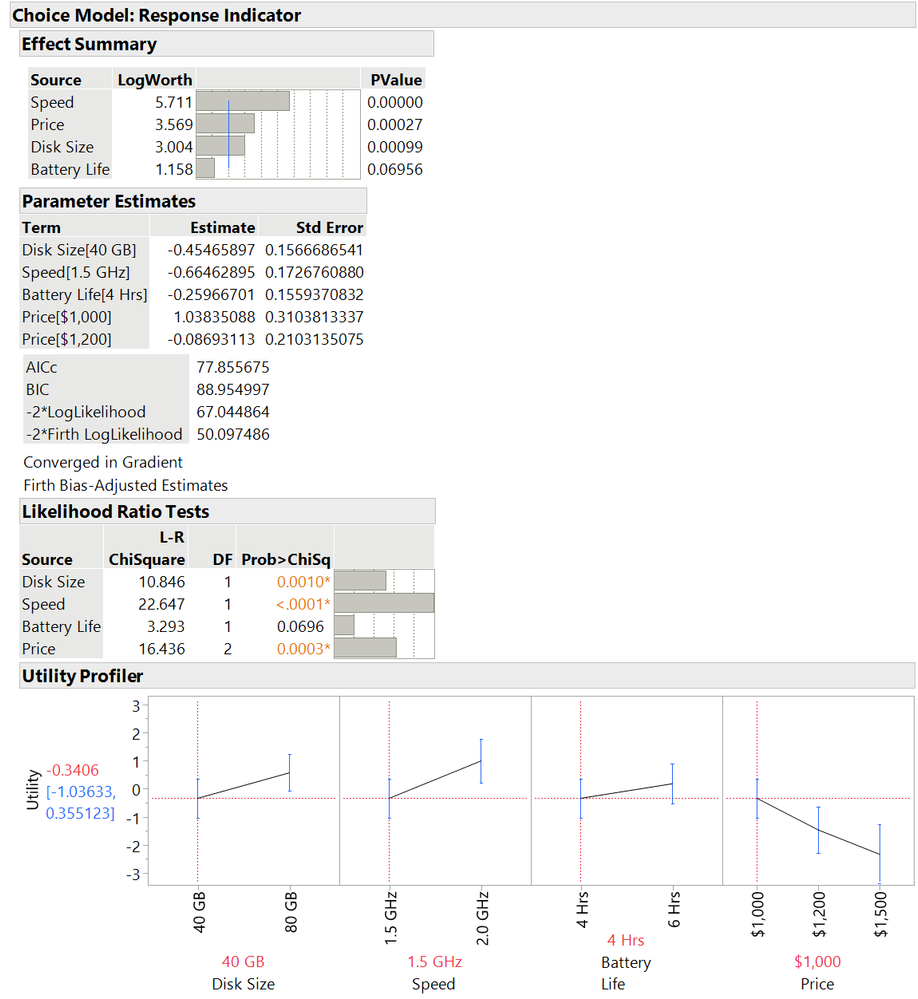
We can use the Utility Profiler to explore results and find optimal settings for the attributes.
MaxDiff Platform
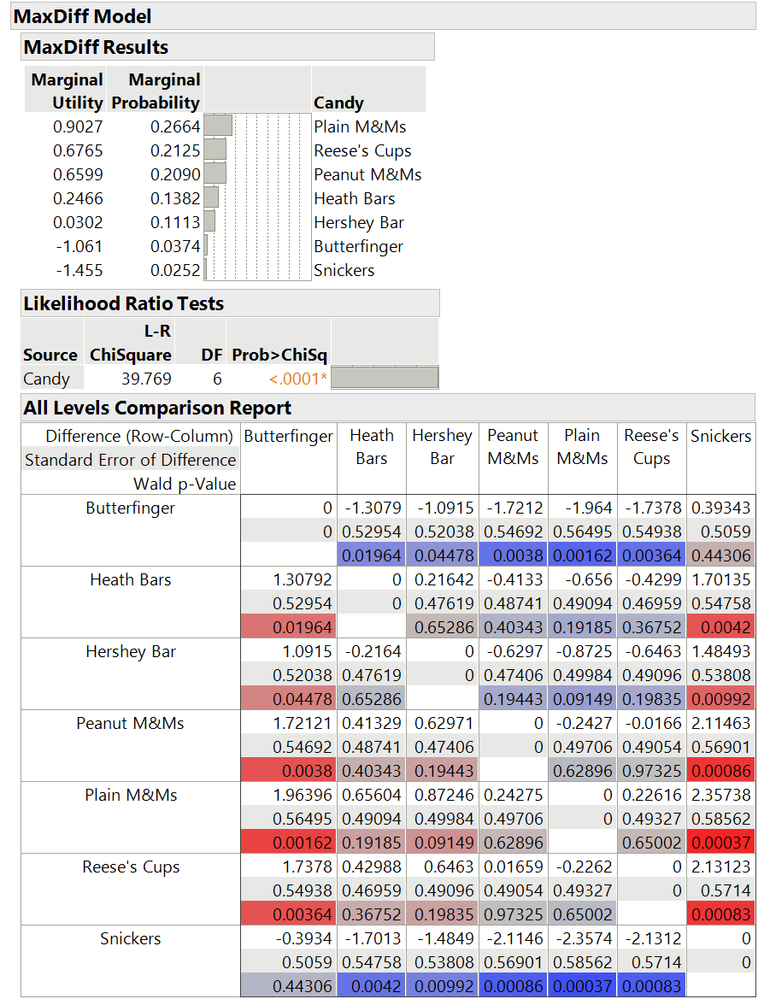
Use MaxDiff (maximum difference scaling) as an alternative to standard preference scales (1 - 10) to determine the relative importance of items being rated. MaxDiff forces respondents to report their most (1) and least (-1) preferred options and none (0) for the others. This often results in rankings that are more definitive than preference scales.
Uplift Platform
The Uplift platform enables you to maximize the impact of your marketing budget by sending offers only to individuals who are likely to respond favorably. It can do this even when you have large data sets and many possible behavioral or demographic predictors. You can use uplift models to make such predictions.
A marketing campaign was designed to increase purchases of a hair coloring product targeting both genders. For purposes of designing the study and tracking purchases, “club card” members of a major beauty supply chain were identified. Approximately half of these members were randomly selected and sent a promotional offer for the product. Purchases of the product over a subsequent three-month period by all club card members were tracked.
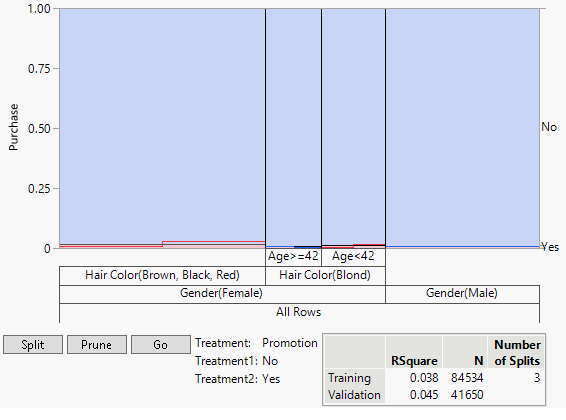
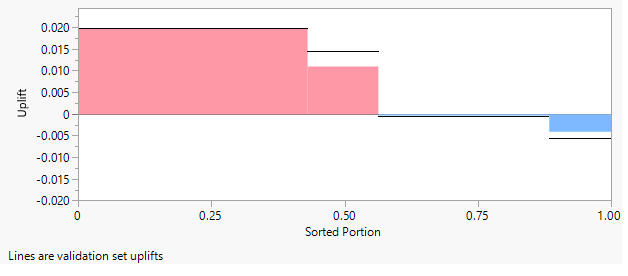
The right hand vertical axis in the graph indicates that the proportion of purchases is small compared to non-purchases. The graph shows that uplift in purchases occurs for females with black, red, or brown hair and for younger females (Age < 42) with blond hair. For older blond-haired women (Age ≥ 42) and males, the promotion has a negative effect.
Multiple Factor Analysis
Multiple factor analysis (MFA) is an analytical method closely related to principal components analysis (PCA). MFA uses eigenvalue decomposition to transform multiple measurements on the same items into orthogonal principal components. These components can help you understand how the items are similar and how they are different.
This example uses data from a simulated sensory panel study of wine characteristics. Participants rated 16 wines on a number of characteristics from 1 (no intensity) to 10 (prominent intensity). You want to better understand how the 16 wines are similar or different.
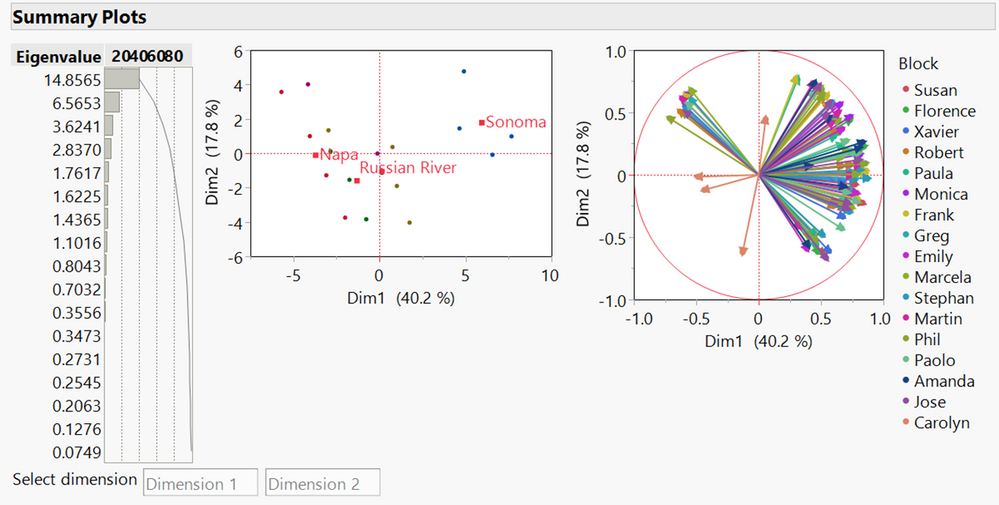
Notice that in the plot of the factor scores in the first two dimensions, the wines tend to cluster together according to their regions. And in the loading plot, the rays in the lower left quadrant correspond to Carolyn. They indicate a difference between Carolyn and the other raters.
1. Market Data Analysis Using JMP 1st Edition, Walter R. Paczkowski. eISBN-13: 9781629604855
2. JMP Online Help Menu - Consumer Research - Behavioural Research Methods
Consumer Research Analysis (1).zip
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.